Osteochondrosis rarely develops in the thoracic region of the spine - the intervertebral discs inside it are smaller and thinner than in the neck or lumbar region. The thoracic region is less mobile, the main load falls on the ribs and sternum.
Unlike cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis, chest symptoms differ only in the location of the pain. The nature and duration of pain are similar. The spinal cord is not affected by prolapse in the thoracic region. Read about this and more.
Stages of pathology
Osteochondrosis usually progresses over time. According to the severity of the manifestation, the pathology is divided into 4 stages.
Preclinical
There are minimal disorders of the spine. Mild pain syndrome may be tension in the back muscles. The development of thoracic pain is possible - chest pain, but this is a rare occurrence.
Discogenic sciatica
There is a change in the structure of the intervertebral discs. Moderate-intensity pain may appear in the affected part of the spine. The patient is effective. But his muscle endurance is declining.
Vascular-radical
At this stage, the annulus fibrosus is completely destroyed. A herniated disc is formed, the process of deformation of the fibrous ring continues, which leads to its rupture. Then the pulposus nucleus falls into the space under the ligaments. A disc herniation occurs. The process affects the tissues located in the disc, disrupts the function of blood vessels, muscles, nerves and ligaments. The disease becomes chronic.
Changes in the shape of bone structure
The spine is rough, the surface is ribbed, uneven. Muscles begin to contract spontaneously, causing limited mobility of the entire spine or a particular vertebra. Pinching of nerves extending from the spinal cord occurs. This leads to a deterioration of impulses from the brain to the body's tissues and organs.
The mobility of the spine as a whole is preserved, but individual vertebrae are fragile and can easily collapse. If the disease is not treated, then it goes to the fourth stage.
Intervertebral disc tissue repair and scar tissue replacement
The damaged intervertebral disc does not perform its functions well, which causes the objects of adjacent vertebrae to converge. This causes abnormalities in the intervertebral joints called spondyloarthritis. In this case, the vertebrae may bend or move relative to their neighbors.
The body activates its own compensation mechanisms. The vertebra straightens and widens in width to relieve the load on the damaged disc. Thus, its area is growing. And the tissue of the collapsed annulus fibrosus can be replaced with bone.
Sometimes it reduces the pain, but as you grow older, the vertebrae make the spinal holes narrower - the nerves constrict.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis often stem from the following factors:
- age of the patient;
- spinal love;
- stage of disease development;
- the patient's condition is remission or exacerbation of the disease.
Symptoms also include:
- radiculopathy - painful damage to the nerve endings of the spinal cord;
- abdominal syndrome;
- heart syndrome, changes in the heart muscle - is characterized by severe pain and does not respond to nitroglycerin;
- pulmonary syndrome: congestion, hypoxia in the lungs;
- paresthesia - a feeling of "gas bubbles" in the body;
- pain in the area of compressed nerves;
- reduced sensitivity to temperature changes and touch;
- impaired motor function of the spine.
The patient's body temperature does not rise. This serves as a sign that allows to distinguish pathology.
The degree of the disease
Lumbaqo
It is a sharp pain that penetrates the body. It manifests itself when lifting heavy objects and other physical activities - the pain is similar to an electric shock.
Morphologically, when the load is too high, an unexpected rupture of the capsule of the intervertebral disc occurs. This traumatic injury leads to nerve irritation - pain.
The muscles are tense and this is well expressed. The lumbar lordosis is smoothed. Thus, the load is redistributed and the intervertebral disc is further compressed, which leads to edema, which increases the pain.
When the pathology is concentrated in the neck, it appears cervical - it manifests itself with pain when turning the head and palpation of the cervical muscles. Exacerbation is often accompanied by cervicocranialgia, which is manifested by a severe headache in the occipital region. There may be tinnitus, dizziness, a feeling of flies in the eyes, toothache.
Dizziness
They occur as a result of narrowing of the spinal canal. Removes and compresses intervertebral disc vessels. The brain cannot get the amount of blood it needs. You may feel a sharp headache, numbness in the hands and shoulders.
Difficulty breathing, which causes the brain to not get enough oxygen. This causes stabbing pain in the heart area.
Intervertebral hernia
At this stage of development, the picture looks very serious - the spinal canal and intervertebral spaces are very narrow. The result can be a hernia - a dangerous defect. Surgery is often needed at this stage of the disease.
Treatment of third-degree osteochondrosis depends on compression of the roots. It is possible to use the same techniques as in the second degree. However, if the pain persists for fifteen days and there are signs of prolapse (vertebral prolapse), surgery is required.
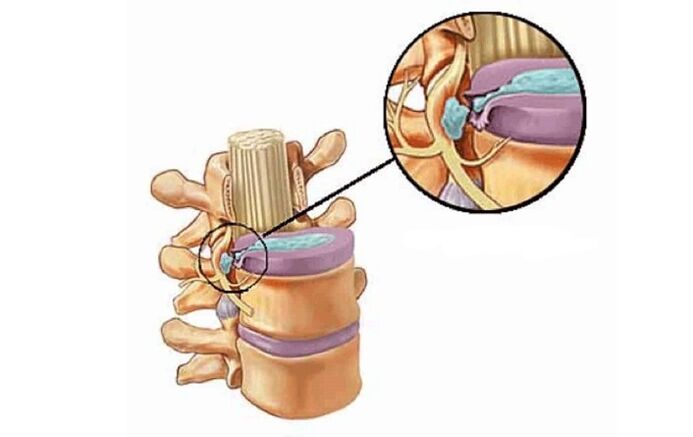
Growths in the vertebrae
As a rule, at this stage of the disease, the hernia disappears, the symptoms of the disease are less pronounced, but the spine is unstable, the vertebrae may slip or bend relative to each other.
In this case, the growth of vertebral bodies can occur - this is called osteophytes. Enlargement causes the spinal nerves to constrict, causing the spinal canal to overlap, known as secondary spinal stenosis. As a result, spinal cord compression is possible, leading to ischemia.
This degree of disease also includes the results of previous operations to remove the hernia. They can manifest themselves as impaired innervation, paresis, inflammation.
Dorsago and dorsalgia
The symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis directly depend on the area of damage to the spine. Dorsalgia and vertebral syndromes of dorsalgia are often different.
Dorsago manifests itself in the form of sudden sharp pain in the chest. This often happens when a person is in a sitting position for a long time without changing posture. Pain can occur when a person's position is physiologically disturbed. In addition, it is possible when performing monotonous work for a long time.
Dorsago is also called "chest lumbago". When this happens, the back and chest muscles become so tense that it becomes difficult to breathe.
Sometimes the pain spreads to the sternum along the ribs and spreads to the scapular area. Sometimes the patient may feel that it is a myocardial infarction. However, no deviations from the norm were detected during the electrocardiogram. If you take nitroglycerin or other means for the heart, there will be no results.

Avoid staying in one position for long. Sedentary work is one of the main causes of osteochondrosis.
Dorsalgia is a mild pain that lasts a long time, sometimes up to those weeks. The inflamed part of the spine causes "dull" pain. This is worrying, so the person usually comes to the doctor.
Dorsalgia can be expressed by:
- the pain is exacerbated when the person takes a deep breath or coughs;
- muscles are overloaded;
- decreased motor activity in the neck or lumbar region;
- have muscle spasms;
- the pain is exacerbated at night and when the person is engaged in physical activity.
Dorsalgia is superior and inferior. First, the main painful manifestations are concentrated in the upper chest and neck. In the second case, it hurts mainly in the sacrum and lower back.
The symptoms of dorsalgia are very similar to the first manifestations of pneumonia. It is important to remember this in order to diagnose the disease in time. If the diagnosis is wrong and treatment is prescribed, the patient's condition will only worsen.
When a woman breastfeeds her baby, she may experience these manifestations of osteochondrosis. It is necessary to treat the disease in this case only by consulting a doctor, taking into account all the nuances.
It is important to measure all the risks of using certain medications to avoid harming your baby and your health.
Atypical symptoms
In some cases, the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis are completely atypical. A person may not even be aware of the disease, because the symptoms are often similar to the symptoms of other pathologies. They should consider in more detail and analyze the situation as a whole:
- the appearance of angina pectoris and pain that mimics the heart that develops during a heart attack is possible; coronary dilatation drugs, such as nitroglycerin, have no effect; and the ECG shows no abnormality;
- with the development of diseases of the mammary glands, pain similar to that that occurs in women may occur; this pain can last for a long time; The examination does not reveal any problems in the mammary glands;
- iliac region and abdomen may be painful, symptoms are not the same as gastritis and colitis; pain under the right rib may be observed, similar to those characterized by hepatitis or cholecystitis; digestion is generally impaired - this is a characteristic symptom of osteochondrosis caused by disorders of the innervation of internal organs; it is necessary to understand what causes the digestive process of food, is it really the cause of thoracic osteochondrosis;
- the process of urination and sexual function may be impaired, because the innervation of the genitourinary system is impaired;
- When thoracic osteochondrosis worsens, there may be long-term, weeks, pain in the sternum, very similar to those present in breast disease; A visit to the mammologist allows you to determine the cause of pain.
These symptoms are associated with back pain, as well as intercostal neuralgia. The onset of atypical symptoms is usually observed in the evening. In the morning, as a rule, there is no bleach. If the right conditions are created for this, the pain increases during the day and causes pain.






















